OLED and AMOLED Which is better for the eyes? Smartphones, TVs, and other gadgets frequently use the display technologies OLED and AMOLED. OLED, which stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode, is a device that emits light when an electric current flows through organic materials.
Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, or AMOLED, adds a layer of thin-film transistors (TFT) to individually control each pixel.

- OLED full form: Organic light-emitting diode
- AMOLED full form: Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode
What Is OLED display?
OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode. It is a type of display that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current passes through them. OLED displays do not need a backlight, so they can produce true blacks and high contrast ratios. OLED displays are also thinner, lighter, and more flexible than LCD displays.
What Are OLED Display Advantages?
OLED is a display technology that has many advantages over other types of displays. Unlike LCD displays, OLED displays do not require a backlight, so they can turn off individual pixels and achieve perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. This also makes OLED displays more energy-efficient and eco-friendly.
What Is AMOLED display?
An AMOLED display is a type of OLED display that uses an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFT) to control the current flowing to each pixel. This allows for faster response times and lower power consumption than passive-matrix OLED displays. AMOLED displays can produce high contrast ratios, deep blacks, and vibrant colors by turning on and off individual pixels made of organic compounds that emit light when electrically activated.
What Are AMOLED Display Advantages?
AMOLED stands for active-matrix organic light-emitting diode. It is a type of display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light and create colors. Some of the advantages of AMOLED displays are:
- They have high contrast ratios, which means they can produce deep blacks and vibrant colors.
- They consume less power than LCD displays, especially when displaying dark colors, because they do not need backlighting.
- They are thinner and lighter than LCD displays because they have fewer layers and components.
- They are flexible and can be curved or rolled, unlike LCD displays, which are rigid and flat.
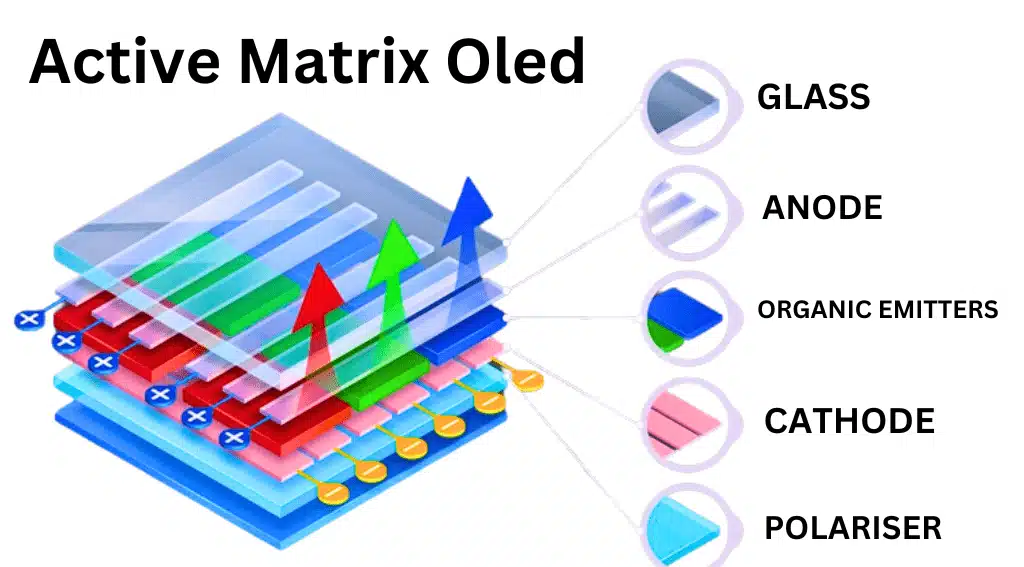
Super AMOLED and OLED explain
OLED and AMOLED both have advantages over conventional LCDs, including greater contrast, broader viewing angles, quicker response times, and lower power usage. But they also have some downsides, including blue light emission and flickering that could harm your eyes.
Blue light is a high-energy visible light that can cause eye strain, migraines, sleeplessness, and possibly damage the retina in the long run. According to some research, OLED displays emit less blue light than LCDs but more than AMOLED displays.
This is because AMOLED displays employ red, green, and blue OLED without color filters, whereas OLED displays use white OLED with color filters. As a result, AMOLED displays have more precise brightness and color temperature controls and emit less blue light.
A screen that flickers is one that changes in brightness noticeably between cycles. It may result in headaches, dry eyes, blurred vision, and tired eyes. Low brightness levels and dark settings make flickering more apparent.
Most OLED displays employ DC dimming, which modifies the current level to change the brightness. Although there is no flickering with this technique, at low brightness levels, there could be color shifts.
Most AMOLED displays employ PWM dimming, which rapidly turns on and off the pixels to change the brightness. Flickering may result from this technique, particularly at low frequencies and brightness levels.
OLED and AMOLED Color Difference
OLED and AMOLED are both display technologies that use organic light-emitting diodes to produce images.
However, AMOLED displays have an active matrix that controls each pixel individually, while OLED displays have a passive matrix that controls a row or column of pixels at a time.
This makes AMOLED displays faster, brighter, and more energy-efficient than OLED displays. However, OLED displays have more accurate and lifelike colors.
while AMOLED displays may have more oversaturated and distorted colors. Therefore, the choice between OLED and AMOLED depends on the user’s preferences and needs.
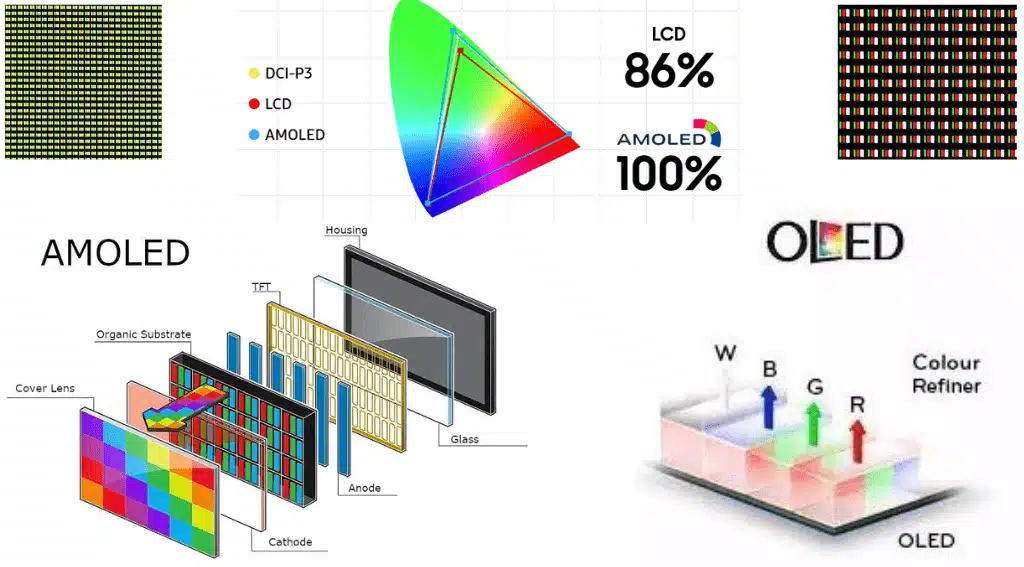
OLED and AMOLED Light Difference
OLED and AMOLED are both display technologies that use organic light-emitting diodes to produce images.
However, AMOLED displays have an active matrix that controls each pixel individually, while OLED displays have a passive matrix that controls a row or column of pixels at a time. This makes AMOLED displays faster, brighter, and more energy-efficient than OLED displays.
However, OLED displays have more accurate and lifelike colors, while AMOLED displays may have more oversaturated and distorted colors. Therefore, the choice between OLED and AMOLED depends on the user’s preferences and needs.
To choose between them, you can consider the following factors: the size and resolution of the screen, the power consumption and battery life of the device, the viewing angle and color accuracy of the display, and the price and availability of the technology.
OLED and AMOLED Display Image Quality Difference
OLED and AMOLED are both display technologies that use organic light-emitting diodes to produce images. However, AMOLED displays have an active matrix layer that allows for faster pixel response times, higher resolutions, and lower power consumption.
OLED displays have deeper blacks and more accurate colors, but they are less flexible and more prone to burn-in. Both types of displays offer high contrast ratios, wide viewing angles, and thin designs.
Decide on the display
Which display is thus more suited to your eyes? Your own preferences and usage patterns may have an impact on the answer. You might choose AMOLED screens over OLED displays if you are sensitive to blue light and frequently use your device in bright conditions.
You may prefer OLED screens over AMOLED displays if you are sensitive to flickering and frequently use your device in dimly lit areas or at low brightness settings. You can also follow some advice to keep your eyes safe from both kinds of displays, like:
- Reduce your exposure to blue light by wearing glasses or using an app that filters it.
- To lessen the brightness and contrast of the screen, choose night mode or dark mode.
- Adapt the screen’s color temperature and brightness to the surrounding lighting
- To relax your eyes, take frequent breaks and blink frequently.
- Maintain an appropriate angle and distance from the screen.
FAQ
Does Apple use OLED or AMOLED?
OLED screens are used in some of Apple’s products. The iPhone 13 boasts an all-screen OLED display, for instance. The Apple Watch, however, makes use of an AMOLED screen. I hope that was helpful. If you have any further inquiries, please let me know.
difference between OLED and AMOLED?
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, while OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. There are some distinctions between OLED and AMOLED, two different display kinds. The following are some distinctions between OLED and AMOLED displays:
1) As compared to OLED, AMOLED uses less electricity and has a higher refresh rate.
2) OLED displays are more accurate in terms of color than AMOLED displays.
3) AMOLED displays are more streamlined and portable than OLED ones.
Is OLED less harmful to the eyes?
Is OLED less harmful to the eyes than LED? This is a question that many people may have when choosing a TV or smartphone display. OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode, and it is a technology that produces very deep blacks and high contrast ratios. LED stands for light-emitting diode, and it is a technology that uses backlighting to illuminate the pixels on the screen.
One of the factors that may affect eye health is blue light, which is a high-energy visible light that can cause discomfort, damage to the retina, and disruption of the circadian rhythm.
According to some studies, OLED displays emit less blue light than LED displays with the same luminance and color temperature. However, there is no strong evidence that blue light from TV or smartphone screens can cause serious eye problems.
Another factor that may cause eye strain is flicker, which is a visible change in brightness between cycles displayed on the screen. OLED displays use low-frequency PWM dimming technology, which means they adjust the brightness through fast flickering.
This can make some people more sensitive to eye strain, especially at low brightness levels. LED displays mostly use DC dimming technology, which means they adjust the brightness by controlling the current. This can cause color shifts at low brightness levels, but it does not produce flicker.
Therefore, the answer to whether OLED is less harmful to the eyes than LED depends on several factors, such as the brightness level, the viewing distance, the content, and the individual sensitivity. There isn’t one answer that works for everyone.
The best way to reduce eye strain from any display technology is to use proper bias lighting, which is a light source behind or around the screen that creates a balanced ambient light and reduces the contrast between the screen and the surroundings.
Bias lighting can also make OLED displays appear brighter and enhance their picture quality. Other ways to protect your eyes from TV or smartphone screens are to use blue light filters, HEV-filtering glasses, or contact lenses, and to take frequent breaks from viewing.
Is OLED better for the eyes than IPS?
OLED and IPS are two types of display technologies that have different advantages and disadvantages for the eyes.
OLED displays have a higher contrast ratio, which means they can produce deeper blacks and more vibrant colors, but they also use low-frequency PWM (pulse width modulation) to adjust brightness, which can cause flickering and eye strain for some people.
IPS displays have a lower contrast ratio, which means they can produce grayish blacks and less vivid colors, but they use high-frequency PWM to adjust brightness.
which is safer for the eyes and reduces flickering. Therefore, the answer to this question may depend on your personal preference and sensitivity to flicker
Why is OLED better than AMOLED?
OLED and AMOLED are both display technologies that use organic light-emitting diodes to produce bright and colorful images.
OLED displays have individual pixels that can turn on and off, resulting in deep blacks and high contrast ratios.
AMOLED displays add an active matrix layer that allows for faster pixel switching and lower power consumption.
OLED displays are more accurate and reliable, but AMOLED displays are more responsive and efficient.