Explanation Poled Display
OLED displays are everywhere these days, from TVs to smartphones. They offer many advantages over traditional LCD screens, such as better contrast, wider viewing angles, and lower power consumption. However, not all OLED displays are the same.
Depending on the materials and methods used to make them, they can have different qualities and characteristics.
In this article, we will explain the difference between POLED and AMOLED, two types of OLED displays that you may encounter in the market.
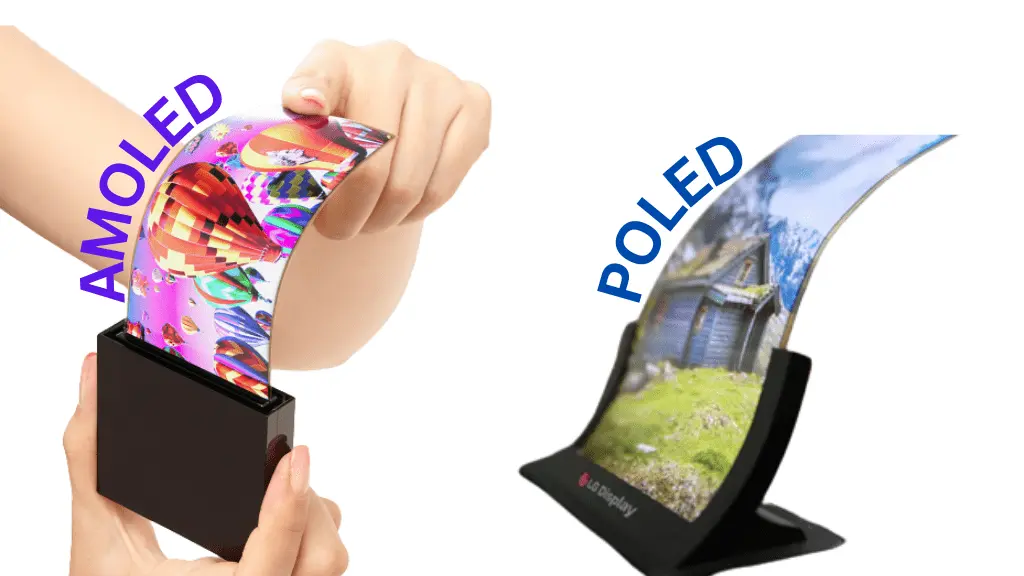

- POLED full form: polymer organic light-emitting diode
- AMOLED full form: Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode.
- HDR full form: high dynamic range.
What Is a Poled Display?
A poled display is a type of OLED display that uses a plastic substrate instead of glass for the organic semiconductor layer.
POLED stands for plastic organic light-emitting diode. The advantage of using plastic is that it makes the display more flexible and durable, allowing for curved, bendable, or even rollable designs.
POLED displays are mainly produced by LG Display, while Samsung Display uses AMOLED (active-matrix OLED) technology for its screens.
What Does POLED Display Mean?
POLED display means plastic OLED display. OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode, which is a type of screen that has pixels made from organic materials that can light up on their own without a backlight. POLED uses a plastic substrate instead of glass, which makes it more flexible, thin, and durable than other OLED screens.
Poled Display Benefits
Poled displays are a type of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) technology that uses self-luminous pixels to create high-quality images. Poled displays have several benefits over other display technologies, such as:
- Higher contrast and brightness: Poled displays can achieve true black levels by turning off individual pixels, resulting in a high contrast ratio and vivid colors. Poled displays also have a wide viewing angle and can produce bright images even in direct sunlight.
- Lower power consumption: Poled displays only consume power when the pixels are lit, which means they can save energy when displaying dark or static images. Poled displays also have a lower operating voltage and a thinner structure than other OLED technologies, which reduces power consumption further.
- Faster response time and refresh rate: Poled displays can switch on and off faster than other display technologies, which reduces motion blur and ghosting effects. Poled displays also have a high refresh rate, which improves the smoothness and clarity of fast-moving scenes and animations.
- Flexible and durable: Poled displays can be made into flexible and bendable shapes, which opens up new possibilities for innovative design and applications. Poled displays also have a high resistance to shock, impact, and temperature changes, which enhances their durability and reliability.
Is pOLED better for eyes?
There is no definitive answer to whether poled displays are good for the eyes or not. Some factors that may affect eye health are the brightness, blue light emission, flicker rate, and resolution of the display.
Poled displays may have higher brightness and lower flicker rates than LCD displays, which could reduce eye strain and fatigue. However, they may also emit more blue light than LCD displays, which could disrupt the circadian rhythm and cause damage to the retina.
Therefore, it is advisable to use poled displays with caution and adjust the settings according to the ambient light and personal preference. It is also recommended to take frequent breaks from looking at the screen and use eye drops if needed.
Which Company Made the First Poled Display?
The first company to make a poled display was LG Electronics. POLED stands for plastic OLED, which is a type of OLED display that uses a flexible plastic substrate instead of glass.
LG introduced POLED technology in 2013 with the launch of the LG G Flex, the first smartphone with a curved display.
How Much High-Quality Video Can the POLED Display Support?
POLED stands for plastic OLED, which is a type of OLED display that uses a flexible plastic substrate instead of a rigid glass one.
POLED displays can support high-quality video with high resolution, contrast, brightness, and color accuracy.
POLED displays can also support fast response times and low power consumption, making them ideal for mobile devices and wearable gadgets.
POLED displays can support video formats up to 4K resolution, depending on the size and pixel density of the screen.
Explanation: Amoled Display
What Is a Amoled Display?
An AMOLED display is a type of OLED display that uses an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFT) to control the current flow to each pixel.
OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode, which means that the pixels produce light and colors by using organic compounds.
AMOLED displays have advantages over LCD displays, such as higher contrast ratios, deeper blacks, more vibrant colors, and lower power consumption when displaying dark images.
What are the benefits of a high contrast ratio?
Higher contrast ratios mean that the display can show a larger difference between the brightest white and the darkest black. This can improve the image quality in several ways:
- It can make images more immersive and realistic, as it can show more details and nuances in both light and dark scenes.
- It can make colors brighter and more saturated, as it can show more shades and variations of each color.
- It can reduce eye strain and fatigue, as it can make it easier to distinguish between different objects and read text on the screen.
What Does AMOLED Display Mean?
It is a type of OLED display that uses an active matrix of thin-film transistors to control the current flowing to each pixel.
This allows for higher resolution, faster response time, and lower power consumption than traditional LCD displays.
AMOLED displays can also produce deeper blacks and more vibrant colors by turning off individual pixels when needed.
Is the AMOLED Display Good for the Eyes?
The AMOLED display is good for the eyes because it emits less blue light than other laptop displays.
More contrast, wider viewing angles, and brighter colors are all provided by this technology, all of which reduce eye strain.
However, some AMOLED displays use low-frequency PWM dimming technology, which can cause flickering and eye fatigue for some sensitive people.
Therefore, it is recommended to use an app or a filter that reduces the amount of blue light and flicker emitted by the screen.
You can also adjust the brightness and color temperature of your display to suit your preferences and environment.
Which company made the first AMOLED display?
The first AMOLED display was developed by Kodak in 2003 and used in its EasyShare LS633 camera.
However, the first AMOLED display to be used in a mobile phone was the BenQ-Siemens S88 handset, which was launched in 2006.
Samsung SDI was one of the main investors in the technology and later introduced the Super AMOLED display, which integrated the touch screen layer into the display itself.
Nokia and Samsung Electronics were also early adopters of this technology on their smartphones.
How Much High-Quality Video Can the AMOLED Display Support?
The AMOLED display can support high-quality video playback up to 8K resolution, depending on the device and the video source.
For example, the Samsung Galaxy S21 Ultra has a 6.8-inch AMOLED display with a resolution of 3200 x 1440 pixels, which can play 8K videos recorded by its own camera or downloaded from online platforms.
Most online streaming services, such as YouTube and Netflix, do not offer 8K content yet, and the internet bandwidth required for 8K streaming is very high. Therefore, most users will not be able to enjoy the full potential of the AMOLED display for video playback.
The AMOLED display also supports high-dynamic range (HDR) video, which enhances the contrast and color range of the image. HDR video can make the scenes look more realistic and vivid, especially on an AMOLED display that has deep blacks and a wide color gamut.
However, not all HDR videos are compatible with all AMOLED devices, as there are different HDR formats such as HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG. Some devices may only support one or some of these formats, while others may support none at all.
Therefore, users need to check the specifications of their devices and the video sources before playing HDR videos on their AMOLED displays.
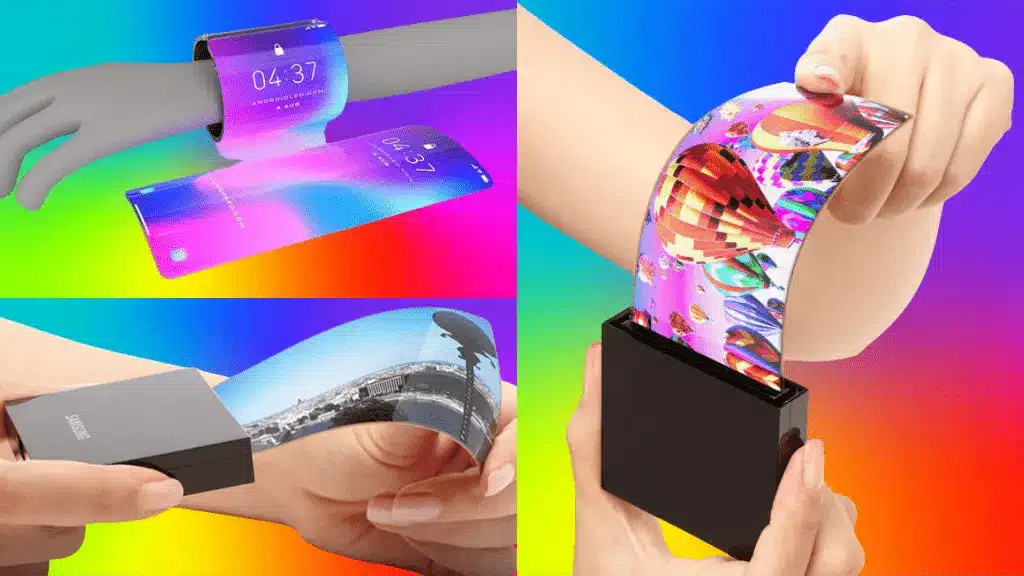

What Is the Difference Between a POLED and an AMOLED Display?
The difference between POLED and AMOLED displays is mainly in the type of substrate they use. POLED stands for Plastic Organic Light-Emitting Diode, while AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode.
Both are types of OLED displays that use organic materials to emit light when an electric current is applied. However, POLED uses a plastic substrate that makes it more flexible, durable, and cheaper than AMOLED, which uses a glass substrate.
AMOLED, on the other hand, has higher brightness, efficiency, and color accuracy than POLED. Both displays have advantages and disadvantages, depending on the user’s preferences and needs.
Poled Vs AMOLED Other Color Comparison
There is no definitive answer to which type of OLED display has better colors, as it may depend on the manufacturer, the device model, the settings, and the personal preference of the user. However, some general comparisons can be made based on the pixel arrangement and the color calibration of the OLED panel. Here are some possible color differences between POLED and AMOLED displays:
- POLED displays use a circular pixel arrangement, which means each pixel has a red, green, and blue subpixel in a circular shape. This may result in more uniform brightness and less color fringing across the screen. However, it may also cause some color shifts and distortion at certain viewing angles, especially for white and gray colors.
- AMOLED displays use a diamond-shaped pixel arrangement, which means each pixel has two subpixels of different colors in a diamond shape. The subpixel colors may vary depending on the manufacturer, but usually they are red-green-blue-green (RGBG) or red-green-blue-white (RGBW). This may result in more accurate and consistent colors across the screen, especially for dark and saturated colors. However, it may also cause some loss of brightness and resolution due to the smaller subpixel size.
- Both POLED and AMOLED displays can produce vivid and lifelike colors with a wide color gamut and high color accuracy. However, the color calibration of the OLED panel may vary depending on the manufacturer and the device model. Some OLED displays may have a warmer or cooler color temperature, a higher or lower contrast ratio, or a more or less saturated color profile. These factors may affect the perceived color quality of the display and may be adjusted by the user according to their preference.
In summary, POLED and AMOLED displays have different pixel arrangements that may affect their color performance in different ways. However, these differences are not very noticeable to the average user and may vary depending on the device model and settings. Both POLED and AMOLED displays can produce vivid and lifelike colors with a wide color gamut and high color accuracy.
Conclusion
Poled and AMOLED are two types of OLED display technologies that have their own pros and cons. Poled displays are more flexible and durable, while AMOLED displays are faster and more efficient. Both offer excellent image quality, vibrant colors, and an infinite contrast ratio. The best choice for you depends on your needs and preferences. We hope this blog post has helped you understand the difference between POLED vs AMOLED and make an informed decision.
Poled Vs AMOLED COMPARISON
Which company made the first curved display?

Curved displays are electronic display devices that feature a concave viewing surface.
They are often marketed as providing an immersive and panoramic experience for viewers. The first company to introduce curved glass displays for smartphones was Samsung with their Galaxy S series and Galaxy Note series devices.
The first company to introduce a curved-screen LED television was Sony with their model KDL-65S990A.
Which display is safe for the eyes?
If you look at the screen for many hours a day, you may wonder which display is safe for your eyes. There are different types of display technologies, such as LCD, LED, IPS, and AMOLED.
Each one has its own advantages and disadvantages for eye health. According to some sources, AMOLED displays have better features for eye care, such as higher contrast ratios, lower brightness levels, and more uniform light distribution.
However, other sources suggest that IPS LCD displays offer more accurate colors and less flickering than AMOLED displays. Ultimately, the best display for your eyes depends on your personal preference and usage habits.
You should also follow some tips to reduce eye strain, such as taking breaks, adjusting the screen settings, and using blue light filters.
Is a 10-bit display good?
A 10-bit display is a type of monitor that can produce more colors than a typical 8-bit display.
A 10-bit display can display up to 1.07 billion colors, while an 8-bit display can only display up to 16.7 million colors.
This means that a 10-bit display can show more subtle shades and gradients of colors, which can enhance the visual quality of images and videos.
A 10-bit display is especially useful for professionals who work with high-resolution graphics, such as photographers, video editors, or designers.
What is an HDR 10 display?
An HDR 10 display is a type of TV screen that supports high-dynamic range (HDR) video.
HDR video has more contrast, brightness, and colors than standard video, making the images more realistic and immersive.
HDR 10 is an open standard that uses static metadata to calibrate the color settings for each video.
It can produce up to 1,000 nits of peak brightness and 10-bit color depth, which means about one billion shades of colors.
HDR 10 is the most common HDR format, and it is compatible with most HDR-capable TVs.