When it comes to choosing between Retina Display and AMOLED for your device, the decision boils down to what you value most in a screen. Both display technologies have their unique advantages and cater to different preferences.

What Is Retina Display
Retina Display, a term popularized by Apple, refers to screens with a high pixel density where pixels are indistinguishable from the human eye at a normal viewing distance.
This results in incredibly sharp and detailed images, making it ideal for users who prioritize clarity and detail in their display.
Retina Display Advantages
Retina displays offer a premium visual experience with their high resolution and pixel density, making images and text appear crisp and detailed. This clarity enhances content consumption and creation, particularly for videos, graphics, and editing tasks. Additionally, the higher pixel density allows for more information to be displayed without compromising quality, which can improve usability and reduce eye strain during prolonged use.
When comparing Retina displays and AMOLED, it’s essential to consider their strengths and weaknesses. Here’s a brief overview:
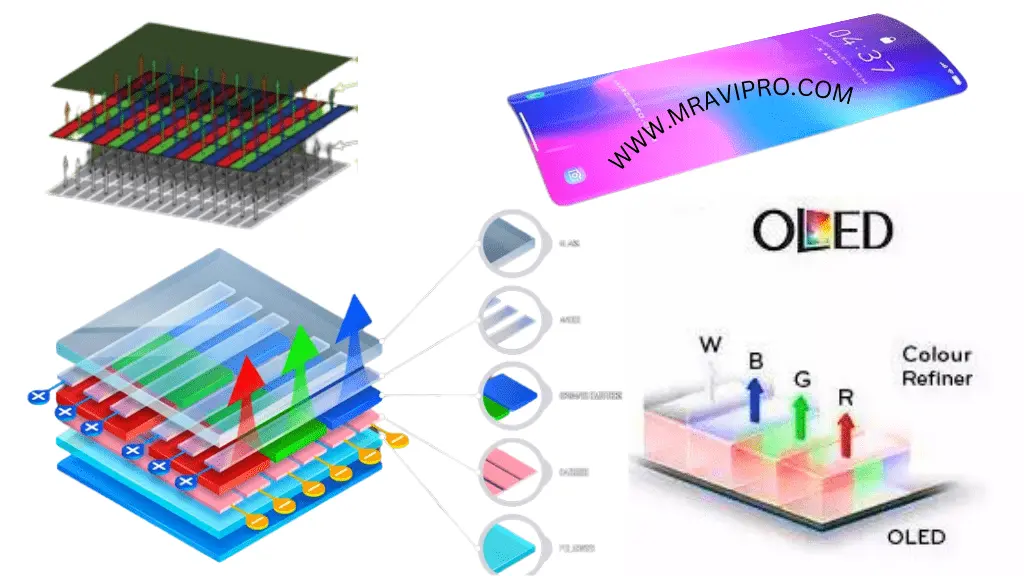
Retina Display:
- Resolution and Brightness: Retina displays, commonly found in Apple devices, offer improved resolution, brightness, and legibility. They provide sharp visuals and are well-suited for tasks like reading text.
- Color Accuracy: While Retina displays are accurate, they may not match the deep blacks and contrast ratios of AMOLED screens.
- Power Efficiency: Retina displays use LCD technology, which can be power-efficient but may not achieve the same energy savings as AMOLED.
- Preference: If you prioritize resolution and legibility, Retina displays are a good choice.
What Is Amoled Display
On the other hand, AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are known for their vibrant color reproduction and deep blacks.
This is because AMOLED screens can completely turn off pixels to produce true black, thereby offering a higher contrast ratio.
This technology is also more power-efficient, as it only lights up the needed pixels, which can contribute to better battery life.
Amoled Display Advantages
AMOLED displays, known for their energy efficiency, consume less power compared to traditional LCD and LED screens. This is because each pixel emits its own light, eliminating the need for backlighting, which can be a significant source of power consumption in other display types. Additionally, AMOLED screens offer a thinner physical profile, which allows for lighter and more flexible devices. They also provide high contrast ratios and vibrant display quality, enhancing the user experience with clearer and sharper images.
AMOLED Display:
- Contrast and Color: AMOLED screens excel in contrast, color accuracy, and deep blacks. Each pixel emits its own light, allowing for true blacks and vibrant colors.
- Energy Efficiency: AMOLED displays are efficient because individual pixels can be turned off when displaying black content.
- Resolution: AMOLED and Retina displays can both achieve various resolutions (720p, 1080p, Quad HD, and 4K).
- Preference: If you value contrast and color accuracy, AMOLED is a strong contender.
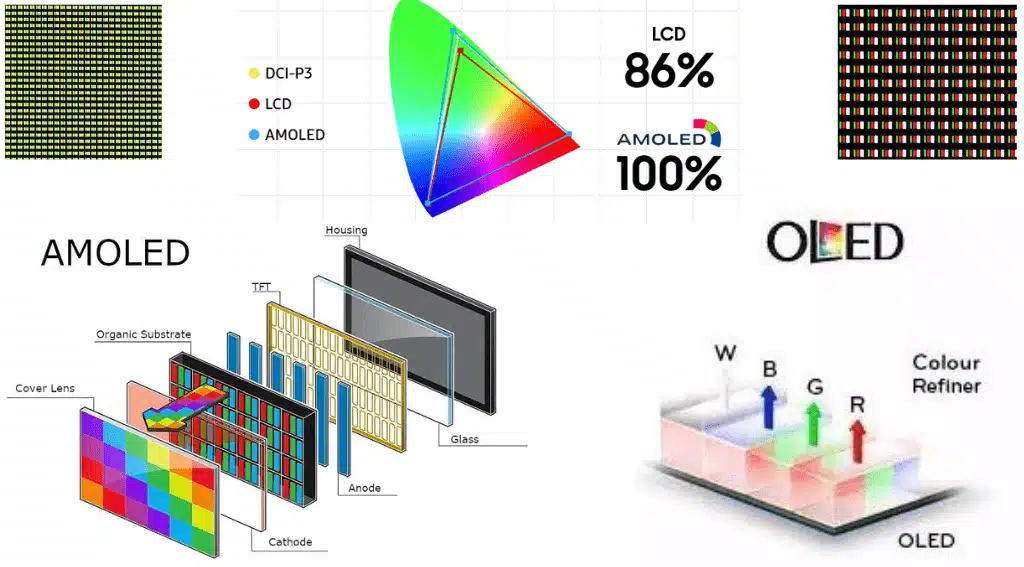
Retina Display Vs AMOLED Display Difference
In terms of brightness and legibility under direct sunlight, Retina Displays generally perform better due to their backlighting, which provides consistent illumination across the screen. AMOLED screens might struggle in this aspect, as they can be less legible under strong ambient light.
Retina Display Vs AMOLED Display Eyes Comparison
For those concerned about eye comfort, the choice isn’t clear-cut. Retina Displays offer a high resolution which can reduce eye strain for some users.
However, AMOLED displays have the advantage of better contrast and color accuracy, which can also be beneficial for visual comfort.
Differences in the Brightness of Light
Ultimately, the “better” display depends on your personal needs and usage. If you’re looking for a screen that offers vivid colors and energy efficiency, AMOLED might be the way to go.
But if you prefer a display with crisp text and bright images even in sunlight, a Retina Display could be more suitable.
It’s worth noting that the technology behind these displays is constantly evolving, with manufacturers striving to combine the best features of both. So, keep an eye out for the latest advancements in display technology to find the perfect screen for you.
Retina Display Vs AMOLED Colors Comparison
When comparing Retina displays and AMOLED screens, the key differences lie in their structure and performance. Retina displays, a term coined by Apple, are known for their high pixel density which results in sharp and detailed images.
On the other hand, AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays are celebrated for their vibrant colors and deep blacks, thanks to their ability to turn off individual pixels, enhancing contrast and energy efficiency.
While Retina displays aim for color uniformity and natural tones, AMOLED screens tend to offer more vivid colors and higher contrast ratios.
Is AMOLED Good for Smartwatches?
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) displays are commonly used in smartwatches. Here’s why they’re good:
- Vivid Colors and High Contrast: AMOLED screens offer punchy, vibrant colors and a high contrast ratio. This means your watch faces and notifications will look sharp and eye-catching.
- Energy Efficiency: AMOLED displays consume less power, especially when showing black colors. Since each pixel emits its own light, black pixels use almost no energy. This makes AMOLED watches more battery-efficient than traditional LCD ones.
- Always-On Mode: Many AMOLED smartwatches support an always-on display mode. Even when the screen dims, you can still see the time and other information without tapping or waking up the watch.
However, there are a couple of downsides:
- Degradation Over Time: The organic materials in AMOLED screens can degrade over extended use. This might lead to fading, decreased brightness, or image burn-ins.
- Cost: AMOLED displays are more expensive to produce compared to LCD screens.
In summary, if you want vibrant colors, energy efficiency, and an always-on display, AMOLED is a great choice for your smartwatch.
Retina Display Vs Amoled Which Is Better 2024
- Choose The Right Monitor For Color Grading 2024 Guide
- Super Retina XDR Display Vs Dynamic Amoled 2x Which Is Better
- Led Vs LCD Which Is Better For Eyes 2023 || Led Vs LCD Difference
- Retina And AMOLED: Which Is Better For Eyes? 2023
What is the difference between a crystal display and a super AMOLED display?
The primary difference between a crystal display, often referred to as an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), and a Super AMOLED display lies in its lighting technology.
LCDs use a backlight to illuminate pixels, which can result in less true blacks and a lower contrast ratio.
In contrast, Super AMOLED displays, an advanced form of AMOLED, have individual pixels that produce their own light, allowing for deeper blacks and a higher contrast ratio.
Super AMOLED displays also integrate the touch sensor and the actual screen, making them thinner and more responsive.
What is the difference between OLED, AMOLED, SuperAMOLED, and Retina Display?
OLED technology is the foundation for several types of displays. OLED stands for Organic Light-Emitting Diode, where each pixel produces its own light, allowing for deep blacks and a high contrast ratio.
AMOLED, or Active Matrix OLED, adds a thin-film transistor to each pixel for faster and more precise control.
Super AMOLED is an advanced version of AMOLED with an integrated touch function and improved visibility in sunlight.
Retina Display, a term coined by Apple, refers to screens with such high pixel density that individual pixels are not discernible at a typical viewing distance, but it’s not a specific technology like OLED or AMOLED.
Are Super AMOLED and Super Retina displays the same?
Super AMOLED and Super Retina displays are not the same. Super AMOLED is a term used by Samsung to describe a display that integrates the capacitive touchscreen layer directly into the display, which makes it thinner.
On the other hand, Super Retina is a term used by Apple and refers to their high-resolution display technology, which is based on LCD and OLED panels with a higher pixel density.
While both offer excellent color and resolution, Super AMOLED displays are known for their better contrast and energy efficiency, whereas Super Retina displays boast higher resolution and pixel density.
Which is better, OLED or Retina display?
Choosing between OLED and Retina displays depends on various factors such as personal preference, usage, and budget.
OLED displays are known for their deep blacks and high contrast ratio because each pixel emits its own light, which can be turned off completely for true black.
Retina displays, a term used by Apple to describe their high-resolution screens, are praised for their color accuracy and clarity.
While OLEDs might offer better contrast, Retina displays are often preferred for their sharpness and detail.
Ultimately, the best choice varies based on individual needs and the specific device in question.
Which display is better than AMOLED?
When it comes to display technologies, AMOLED is known for its vibrant colors and deep blacks, thanks to its ability to control pixels individually.
However, newer technologies like QD-OLED and LTPO AMOLED offer improvements in various aspects.
QD-OLED combines the benefits of OLED with quantum dots to enhance brightness and color accuracy.
LTPO AMOLED, on the other hand, provides better power efficiency, especially with high refresh rates.
Ultimately, the choice of display depends on the specific needs and preferences regarding color accuracy, brightness, power consumption, and refresh rates.
what is LTPO AMOLED display?
LTPO technology, which is low-temperature polycrystalline oxide, is a display technology that allows for variable refresh rates.
This means the display can adjust how often it updates per second, which can range from 1Hz to 120Hz and beyond.
The advantage of LTPO is that it can conserve battery life by lowering the refresh rate when full motion isn’t necessary, such as when viewing static images or text.
This technology combines the high refresh rate capabilities of LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon) with the energy efficiency of IGZO (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide) to provide an optimal balance between performance and power consumption.