The S8050 transistor is a general-purpose NPN transistor that can be used for audio amplification, switching, and low-signal applications. It has a maximum collector current of 1.5A and a maximum collector-emitter voltage of 25V. Some of its equivalent transistors are 2N5830, S9013, S9014, 2N5551, and SS8050. The S8550 is a PNP transistor that complements the S8050.
S8050 Transistor Details and Features
- This NPN transistor is bipolar.
- The range of current gains is 40 to 400hFE
- 700 mA is the collector current (IC).
- 30V is the collector-to-base voltage (VCB).
- 20 volts is the collector-to-emitter voltage (VCE).
- 5V is the emitter’s base voltage (VEB).
- 150°C is the junction temperature (TJ).
- The transistor’s power dissipation is 1W.
- 100 MHz is the transition frequency (FT).
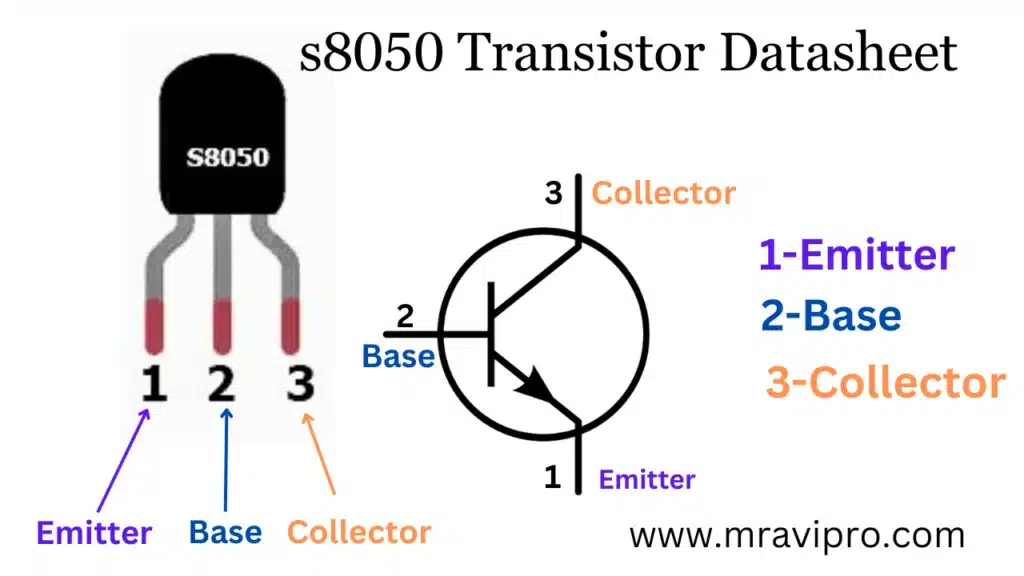
S8050 Transistor Pinout
The S8050 transistor is a low-voltage, high-current NPN transistor commonly used in audio amplification and switching applications. The pinout of the S8050 transistor is as follows:
| Pin | Pin Name | Details |
| 1 | Emitter | Current drains out through this terminal |
| 2 | Base | Controls the biasing of the transistor |
| 3 | Collector | Current flows in through this terminal |
Where is the S8050 transistor used?
The S8050 transistor is a versatile device that can be used for various purposes in electronic circuits. Some of the common applications of the S8050 transistor are:
- Audio amplification circuits: The S8050 transistor can be used to amplify audio signals from microphones, speakers, headphones, etc. It has a high gain value and can operate at low voltages, making it suitable for audio applications.
- Class B amplifiers: The S8050 transistor can be used in a push-pull configuration with its complementary PNP transistor (S8550) to form a class B amplifier. A class B amplifier is a type of multistage amplifier that is commonly used for loudspeakers. It has high efficiency and low distortion but requires two transistors for each half-cycle of the input signal.
- Push-pull transistors: The S8050 transistor can be used as a push-pull transistor in various circuits that require high current and low voltage switching. A push-pull transistor is a pair of transistors that are connected in such a way that one transistor is on when the other is off, and vice versa. This allows the circuit to switch between two states (high and low) with minimal power loss.
- Circuits where high gain is required: The S8050 transistor has a maximum gain value of 400, which means that it can amplify the input signal by 400 times. This makes it useful for circuits where high gain is required, such as sensors, detectors, oscillators, etc
- Low-signal applications: The S8050 transistor can also be used for low-signal applications, such as LED control circuits, light sources, and other electronics. It can handle currents up to 700mA and voltages up to 20 volts, which are sufficient for most low-signal applications
S8050 Transistor Description
The S8050 transistor operates as a low-voltage, high-current transistor device in use. SS8050 transistors have more circuits and different applications.
Amplifier and voltage regulator circuits primarily concern current gain values, ranging from 40 to 400 hFE for the S8050 transistor.
The S8050 transistor’s maximum collector current value was 700 mA; this value determined the maximum load that the transistor could withstand.
The S8050 transistor had a maximum power dissipation of 1 watt, which was used to calculate the amount of power that could be removed from the device without causing any harm.
This S8050 transistor’s switching frequency, which is 100 MHZ, is crucial for switching applications. 150°C is the transistor heat of an S8050 transistor.
S8050 Transistor Datasheet PDF Download
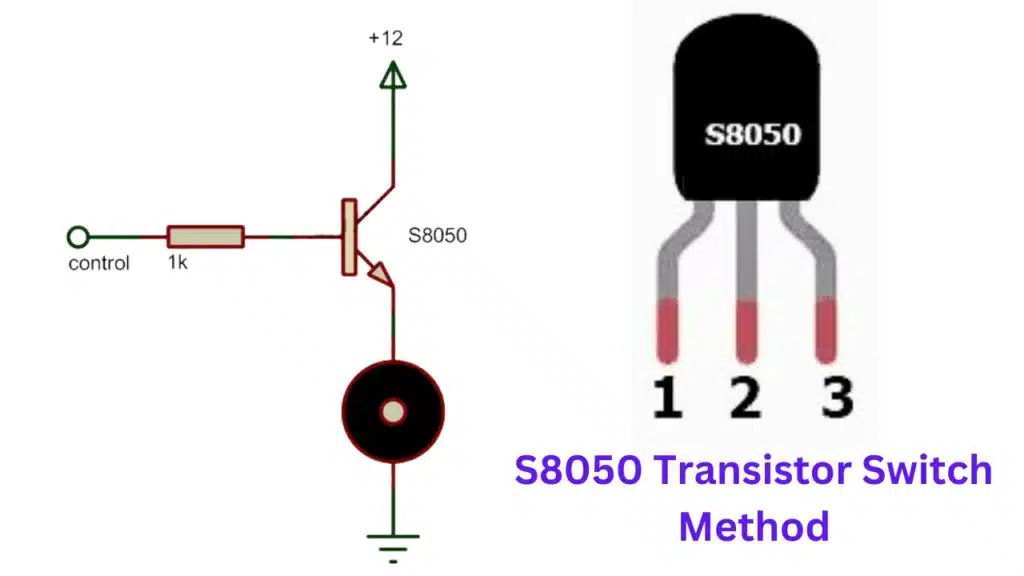
S8050 Transistor Switch Method
The S8050 transistor is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor that can be used as a switch in electronic circuits. It has a collector current of up to 700 mA and a collector-emitter voltage of up to 20 V. The S8050 transistor can be easily controlled by applying a small current to its base terminal, which allows it to switch larger currents or voltages across its collector and emitter terminals. The S8050 transistor is widely used in applications such as relay drivers, LED drivers, audio amplifiers, and motor controllers.
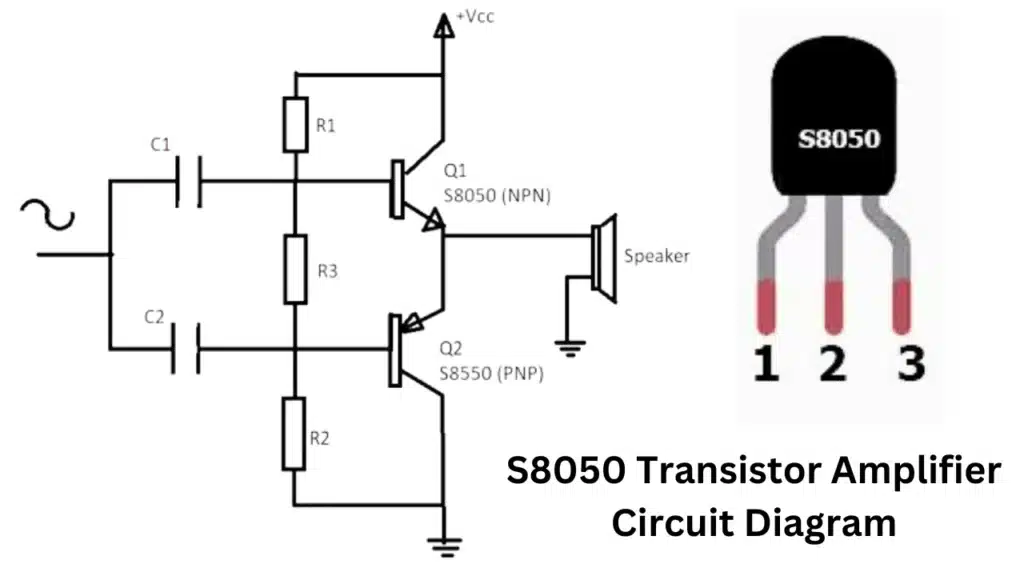
S8050 Transistor Amplifier Circuit Diagram
A S8050 transistor is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that can be used as a switch or an amplifier in electronic circuits. A typical S8050 transistor amplifier circuit diagram consists of three main components: the S8050 transistor, a biasing resistor, and a load resistor. The biasing resistor is connected between the base and the emitter of the transistor, and it sets the operating point of the transistor. The load resistor is connected between the collector and the power supply, and it determines the output voltage and current of the amplifier. The transistor’s base receives the input signal, which is then applied, and the transistor’s collection receives the amplified signal.
- What is PNP VS NPN Transistor Difference 2023
- The Best Bc547 Transistor Datasheet PDF Download
- IRFZ44N Mosfet Datasheet Full Details
- RU6888r Mosfet Datasheet
FAQ
S8050 transistor datasheet pdf download
If you are looking for an S8050 transistor datasheet in PDF format, you can download it from the link below.
The S8050 is a low voltage, high current, small signal NPN transistor intended for use in both general-purpose applications and Class B push-pull audio amplifiers.
The datasheet provides the electrical characteristics, pin configuration, package outline, and typical applications of the S8050 transistor.
What is the difference between S8050 and BC547?
The S8050 and BC547 are both NPN transistors that can be used for amplification or switching purposes. However, they have some differences in their ratings and characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. According to, the main differences are:
The S8050 has a higher collector current (Ic) of 1500mA, while the BC547 has a lower Ic of 100mA. This means that the S8050 can drive heavier loads than the BC547.
The BC547 has a higher collector-emitter voltage (Vceo) of 45V, while the S8050 has a lower Vceo of 25V. This means that the BC547 can withstand higher voltages than the S8050.
The BC547 has a higher transition frequency (fT) of 300MHz, while the S8050 has a lower fT of 100MHz. This means that the BC547 can operate faster than the S8050 in high-frequency circuits.
s8050 transistor as a switch
The S8050 is an NPN transistor that can be used for switching and amplification purposes.
It can handle a maximum collector current of 700mA, which is enough to drive various loads such as LEDs, relays, and bulbs.
To use it as a switch, the base terminal must be biased with a small current to turn on the transistor and allow the current to flow from the collector to the emitter.
s8050 transistor vs. 2n2222
The S8050 and 2N2222 are both NPN transistors that can be used for low-power amplification and switching circuits. However, they have some differences in their ratings and characteristics.
The 2N2222 can handle higher collector current (800mA) and frequency (300MHz) than the S8050 (100mA and 100MHz respectively). The S8050 can handle higher power dissipation (1000mW) than the 2N2222 (625mW).
The pin configurations of both transistors are identical, so they can be replaced in a circuit without changing the wiring. However, the load current and frequency requirements of the circuit should be considered before replacing one transistor with another.